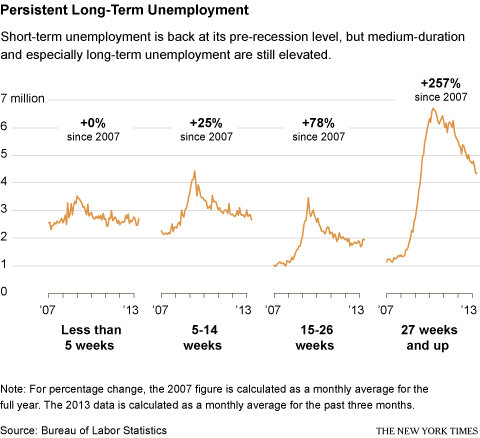
Long-term unemployment remains a very dark shadow in the May jobs report: 4.4 million workers have been out of a job for more than six months. In essence, the job market has normalized for the short-term unemployed. But the longer you have been out of a job, the bleaker the picture gets.
The number of people who report being out of work for less than five weeks has returned to almost the same level as in 2007. But the number of people unemployed 5 to 14 weeks is about 25 percent higher. For those out of a job 15 to 26 weeks, it is 78 percent higher. And the number of long-term jobless, those unemployed for more than 27 weeks, is a whopping 257 percent higher.
The long-term unemployed are struggling mightily to get rehired, as confirmed by recent research by Rand Ghayad and William Dickens of the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston. Some economists have theorized that the unusually long spells of unemployment we have seen in the wake of the recession are caused by a “mismatch”: The long-term jobless were in obsolete professions, with obsolete skills, and that is why they are not getting new gigs.
But Mr. Ghayad and Mr. Dickens argue that is not the case. The long-term jobless seem to be having trouble finding work across industries, for instance. Discrimination does seem to be a major factor, though: Employers simply do not want to hire the long-term jobless, as my colleague Catherine Rampell has reported and further research by Mr. Ghayad has shown.
Granted, the number of long-term jobless has come down sharply over the last three years, declining to a current level of 4.4 million from a high of 6.7 million in early 2010. Much of that reduction came about because the long-term jobless found jobs — it is not just about workers dropping out of the labor force. Still, the reality remains that the longer a worker is out of a job, the slimmer and slimmer the chance of being rehired.
Article source: http://economix.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/06/07/long-term-jobless-still-a-bleak-picture/?partner=rss&emc=rss