
CATHERINE RAMPELL
Dollars to doughnuts.
Adam Looney and Michael Greenstone at the Hamilton Project have put together a beautiful chart illustrating once again why college is worth it, despite the current fad of claiming otherwise.
It shows the share of people at each income level who had various levels of educational attainment:
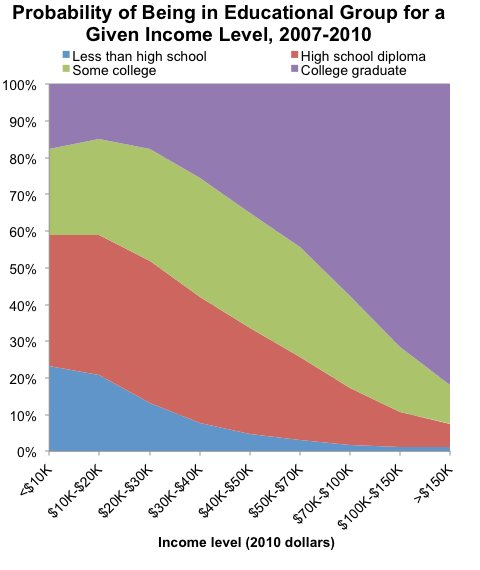 Adam Looney and Michael Greenstone, the Hamilton Project
Adam Looney and Michael Greenstone, the Hamilton Project
As you can see, the more income you earn, the more likely you are to have gone to college.
Of the Americans who earn over $150,000, 82 percent had a bachelor’s degree. Just 6.5 percent had no more than a high school diploma. And while there are lots of stories about broke college grads, people with higher education are much less likely to have low incomes than those without degrees.
Sure, you say, but people graduate from college with a lot of debt, which must surely wipe out their higher earnings!
Even factoring in the debt, though, college is still a great investment. Here’s another chart worth a million words, also from Mr. Looney and Mr. Greenstone, that shows the return on investment for going back to school compared to investing that same tuition money in the stock market, long-term Treasury bills, housing, corporate bonds or gold:
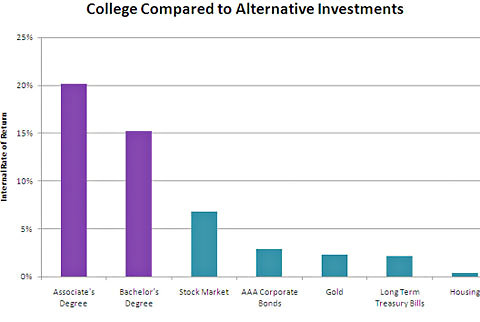 Adam Looney and Michael Greenstone, the Hamilton ProjectAsset returns are geometric averages since 1950. Long-term Treasury bills have 10-year maturities after 1953. Source: Authors’ calculations of internal rate of return, values adjusted for inflation using C.P.I.-U; March Current Population Survey 2007-10 averages; National Mining Association; National Center for Education Statistics; Robert Shiller online data; Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Adam Looney and Michael Greenstone, the Hamilton ProjectAsset returns are geometric averages since 1950. Long-term Treasury bills have 10-year maturities after 1953. Source: Authors’ calculations of internal rate of return, values adjusted for inflation using C.P.I.-U; March Current Population Survey 2007-10 averages; National Mining Association; National Center for Education Statistics; Robert Shiller online data; Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Nothing guarantees financial success, of course. But at the very least, postsecondary education opens the door to higher-paying jobs that are not available to people with fewer skills.
Article source: http://economix.blogs.nytimes.com/2012/09/17/college-still-worth-it/?partner=rss&emc=rss